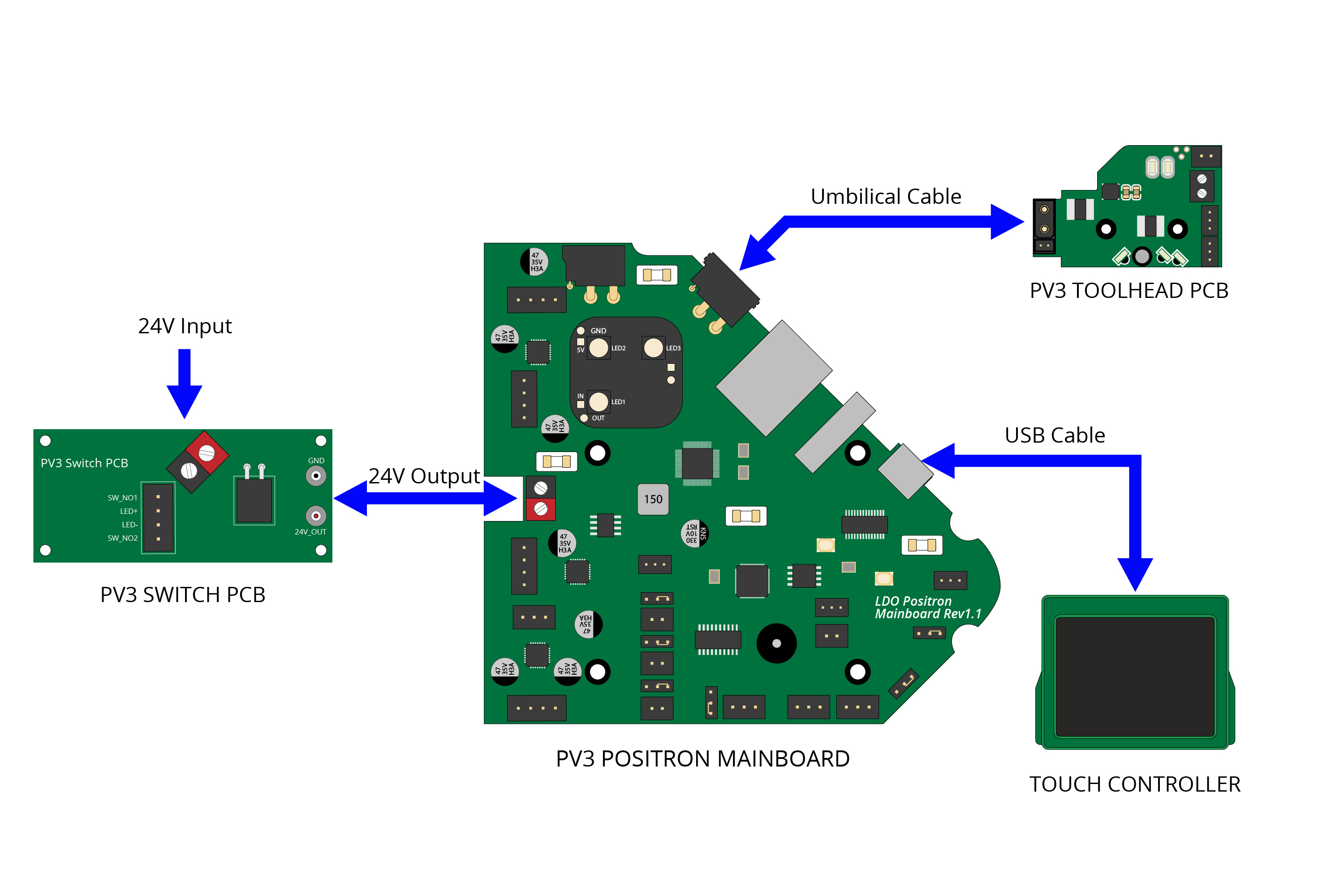
¶ System Overview
The Positron system consists of three PCBs, a touch controller and the umbilical cables. A simplified wiring diagram is shown below:
- LDO Positron Mainboard, It is a motherboard specifically designed for PV3.2 kits. It features Raspberry Pi Arm Cortex-M0+ RP2040 MCU, with 4 TMC2209 stepper drivers and 3 fan ports. It also features an onboard USB hub which expands the RPI host connectivity with ethernet and an USB A port.
- PV3 Toolhead PCB, It is a toolboard PCB specifically designed for the PV3.2 kits. It features RP2040 MCU and ADXL345 accelerometer all integrated into one board.
- PV3 Switch PCB, It controls the printer switch and reduce the current thus preventing the switch from overheating.
- Umbilical Cable, It is a custom flex cable that is rated for drag chain use. It delivers 24V power to the toolhead PCB while also carrying USB data.
- PV3 Touch Controller, It features a touch screen with a Raspberry Pi CM4.
¶ Features
- Convenient wiring, wire up the entire printer with a few simple cables.
- USB Klipper connection, no additional software or hardware setup.
- Exposed Connectivity, with a PCB form factor designed specifically for the Positron, USB and ethernet ports are directly exposed and allow for easy connections
¶ Klipper Config Files
A Klipper Configuation can be found in the PositronHardware github repo here.
¶ Port and Pin Definitions: LDO Positron Mainboard
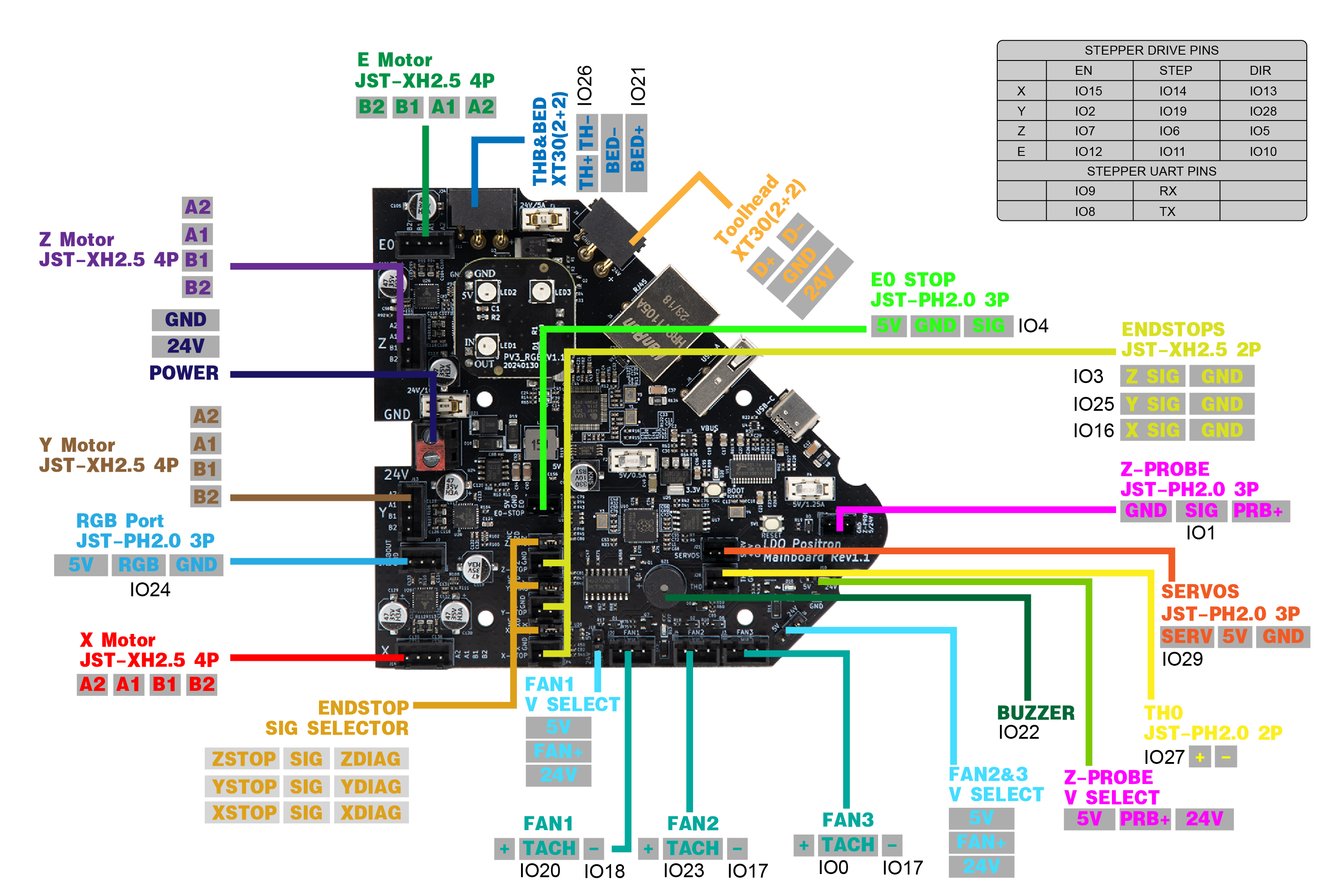
| Device/Port | PCB Label | Connector Type | RP2040 Pin | Description |
| X/Y/Z Endstop | Endstop | JST-XH2.5 2P | gpio16/25/3(X/Y/Z) | Connects to the X, Y and Z endstop. X endstop is gpio16, Y endstop is gpio25 and Z endstop is gpio3 . |
| E0 Endstop | Endstop | JST-PH2.0 2P | gpio4 | Connects to the E endstop. |
| X Motor | X | JST-XH2.5 4P | gpio14/13/15/8/9 (step/dir/ena/uart/tx) | A stepper motor port for the X Motor. |
| Y Motor | Y | JST-XH2.5 4P | gpio19/28/2/8/9 (step/dir/ena/uart/tx) | A stepper motor port for the Y Motor. |
| Z Motor | Z | JST-XH 2.5 4P | gpio6/5/7/8/9 (step/dir/ena/uart/tx) | A stepper motor port for the Z Motor. |
| E Motor | E0 | JST-XH 2.5 4P | gpio11/10/12/8/9 (step/dir/ena/uart/tx) | A stepper motor port for the E Motor. |
| Fan | Fan1/2/3 |
Fan1: gpio18/20 (fan/tacho) Fan2: gpio17/23 (fan/tacho) Fan3: gpio17/0 (fan/tacho) |
Connects to cooling fans. | |
| Z-Probe | Z-PROBE | JST-PH2.0 3P | gpio1 | Probe for bed leveling and/or Z sensing. |
| Neopixel | RGB | JST-PH2.0 3P | gpio24 | Connects to neopixel LEDs. |
| Buzzer | BUZZER | N/A | gpio22 | Connects to Buzzer. |
| Hotend Thermistor | TH0 | JST-PH2.0 2P | gpio27 | Connects to the hotend heater. Uses a 2.2kΩ pull up resistor. |
| SERVOS | SERVOS | JST-PH2.0 3P | gpio29 | Connects to the servos. |
| THB& BED | THB& BED | XT30(2+2) | gpio26/gpio21 | Connects to the heatpad. Uses a 4.7kΩ pull up resistor. |
| Toolhead Cable | XT30(2+2) | An USB port for toolhead. | ||
| Z-Probe V Selector | Selects the supply voltage of the Z Probe. Selection of 24V or 5V. | |||
| Fan/1/2/3 V Selector | Selects the supply voltage of the fans. Selection of 24V or 5V. | |||
| Endstop SIG Selector | Selects the supply voltage of the endstop. Selection of STOP or ADIG. |
¶ Port and Pin Definitions: PV3 Toolhead PCB
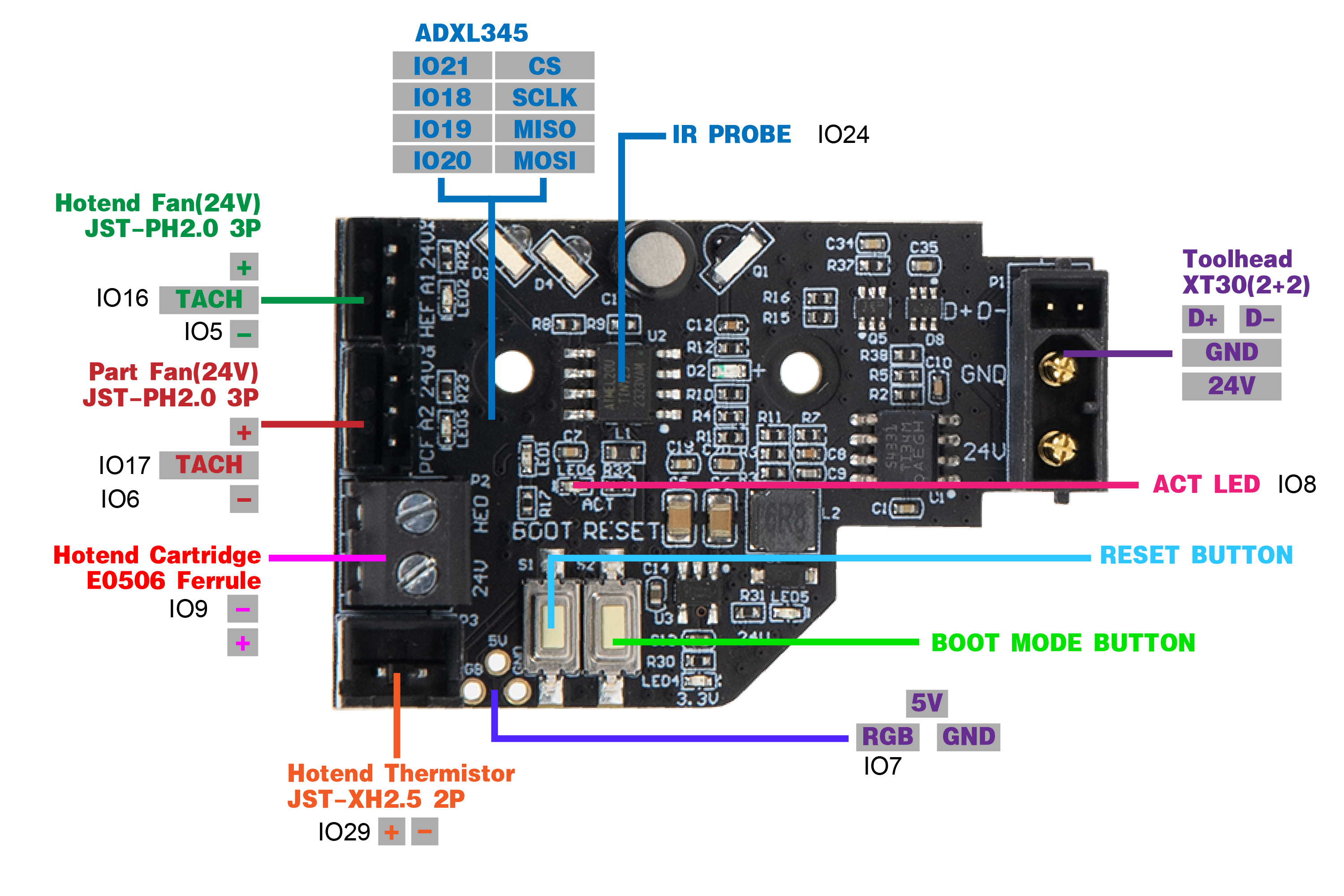
| Device/Port | PCB Label | Connector Type | RP2040 Pin | Description |
| Hotend Heater | HE0 | E0506 Ferrule | gpio9 | Connects to the hotend heater. |
| Hotend Thermistor | TH0 | JST-XH2.5 2P | gpio29 | Connects to the hotend thermistor. Uses a 2.2kΩ pull up resistor. |
| Part Fan | PCF | JST-PH2.0 3P | gpio6/17 (fan/tacho) | Connects to part cooling fan. The fan control pin is gpio6 and the tachometer sensor pin is gpio17. |
| Hotend Fan | HEF | JST-PH2.0 3P | gpio5/16 (fan/tacho) | Connects to hotend fan. The fan control pin is gpio5 and the tachometer sensor pin is gpio16. |
| IR Probe | PROBE | N/A | gpio24 | Connects to the probe. |
| Neopixel | GRB | N/A | gpio7 | Connects to neopixel LEDs. |
| Toolhead | XT30(2+2) | An USB port for toolhead. | ||
| Accelerometer | N/A | N/A |
gpio21/18/20/19 (cs/clk/mosi/miso) |
ADXL345 accelerometer for input shaping. Controlled via software SPI. |
| Activity LED | ACT | N/A | gpio8 | A small software controlled onboard LED. Active low. |
¶ Electrical Specifications
| Parameter | Symbol | Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Unit | Comments |
| Power Supply Input | Vin | 20 | 24 | 28 | V | power input for the toolboard. |
| 5V Current | Irpi | 5 | A | current output for the 5V buck converter. | ||
| Fan Current | Ifan | TBD | A | current rating for each fan port (HEF and PCF). | ||
| Bed Current | Ihe | TBD | A | limited by max. continuous current of mosfet. | ||
| Hotend Current | Ihe | TBD | A | limited by max. continuous current of mosfet |
¶ Firmware Setup and Update
The firmware for Positron consists of two components: Katapult and Klipper. Katapult is a bootloader designed specifically for Klipper, it ensures that the software on the RP2040 MCU boots up smoothly and allows for easy updating of the Klipper firmware. You can learn more about Katapult here. Klipper is the main firmware that runs on the RP2040 MCU, you can learn more here.
Your Positron will come shipped with both Katapult and Klipper installed. Ideally, you will only ever need to occasionally update the Klipper firmware and never have to touch Katapult. If the Katapult bootloader was erased or is not present for any reason, you can check this section for instructions on how to reupload Katapult.
¶ Hardware Setup
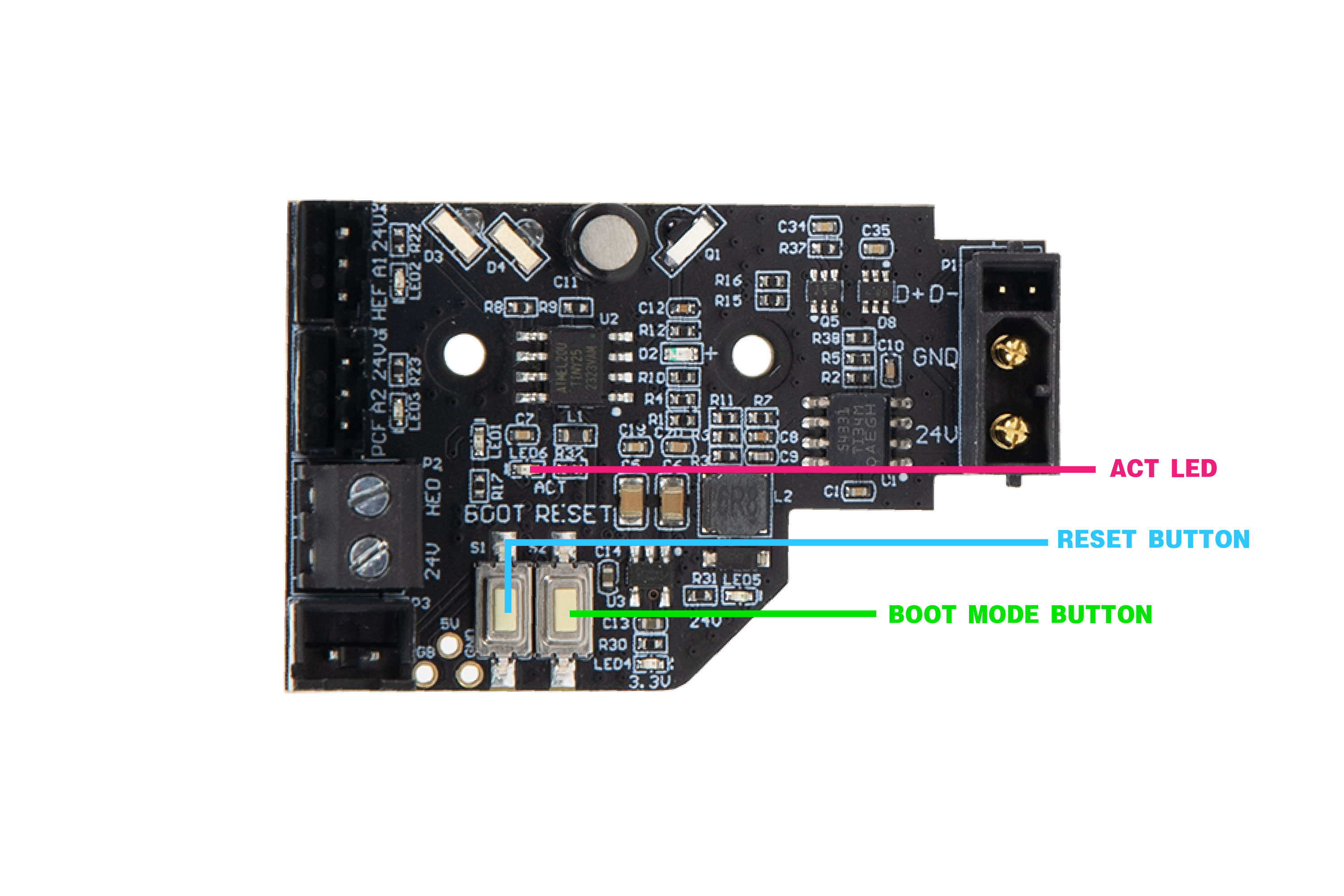
No special setup is required for installing either Klipper or Katapult. Positron simply needs to be hooked up as it operates normally in your 3D printer, with the boards connected to your Klipper host device (e.g. Raspberry Pi). You also need access to the two buttons (RESET and BOOT0) on the boards.
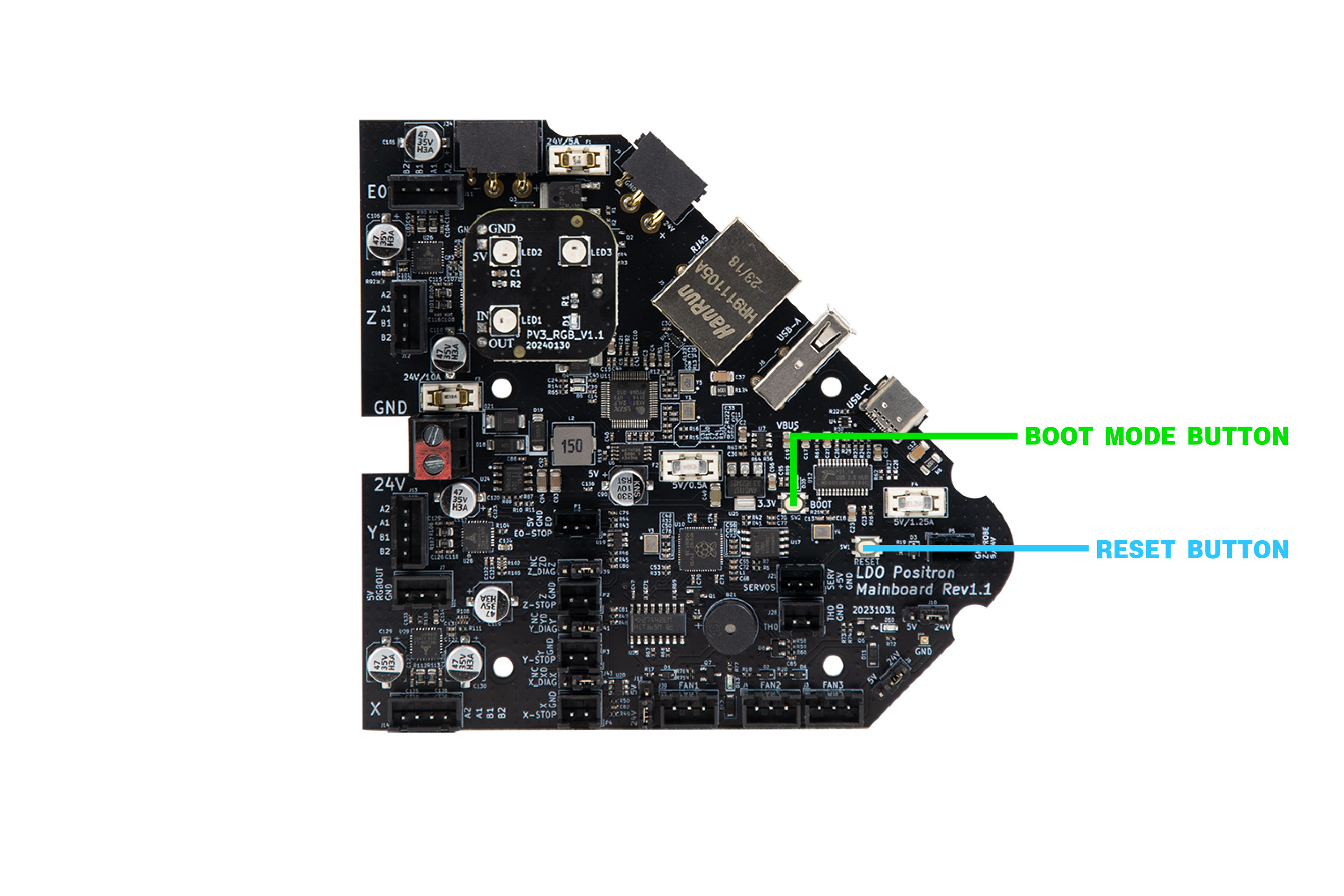
PV3 Toolhead PCB comes with an ACT indicator light, which will be important later. Reference the photo below to find the buttons and LEDs.
¶ Compiling Klipper Firmware
The following instructions are for compiling and upload new Klipper firmware to your board. You need to perform these steps if you want to update your klipper firmware to the newest version or if you are doing a fresh install and just uploaded Katapult (see the previous sections). Before compiling the firmware, you will need to have Klipper already installed on your host device (e.g. Raspberry Pi).
- Log on to your Klipper host via SSH, windows users can use putty or any other SSH client. Mac and Linux users can simply connect with the
sshcommand in their command line terminal. Run the following commands to open the firmware configuration interface:
cd ~/klipper
make menuconfig
- In the configurator, Enable extra low-level configuration options, choose Raspberry Pi RP2040, match the rest of the settings with the screenshot below:
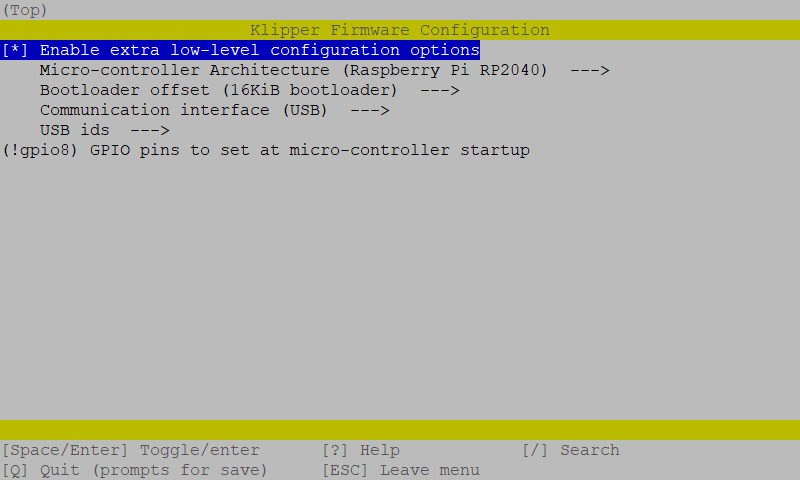
- Most importantly, make sure you set the
16KiB bootloaderoffset. Otherwise you will erase the Katapult bootloader! - Enter
Qto quit and confirm withYes when prompted to save. And run the following to generate the firmware file:
make clean
make
- A firmware file called will now be generated and can be located in the directory
~/klipper/out. You are now ready to upload this firmware to the board. The recommended method is uploading via themake flashcommand.
¶ Uploading Klipper (via make flash)
- Run
ls /dev/serial/by-idto find the USB ID of your board. The USB ID should have a format similar to this:usb-Klipper_rp2040_1234567890000000-if00. - Run the following commands. This will install the
python,pip, and thepyserialpython module if it is not present. You may receive anerror: externally managed environmentwhen running the last command. This simply meanspyserialhas already been installed and you may move on to the next step.
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
pip install pyserial
- Run the following commands to upload the firmware to the MCU directly:
cd ~/klipper
sudo service klipper stop
make flash FLASH_DEVICE=/dev/serial/by-id/<your USB ID>
sudo service klipper start
- If you encounter any connection issues after flashing the new firmware, reboot your printer. Your board should now have the newest firmware. If the flashing process failed, you may want to try using the the second method and upload Klipper via Katapult.
¶ Uploading Klipper (via Katapult)
In this section we will use an alternative method to upload klipper firmware using the Katapult bootloader. If your boad is missing the Katapult bootloader for any reason, you should follow the next section to install it first.
- First we will check and install the Katapult package (if necessary):
test -e ~/katapult && (cd ~/katapult && git pull) || (cd ~ && git clone https://github.com/Arksine/katapult) ; cd ~
- To upload Klipper, we will use a Python script to communicate with the Katapult bootloader inside of the board. First, we will first need to setup a Python3 environment. Run the following:
virtualenv -p python3 ~/katapult-env
~/katapult-env/bin/pip3 install pyserial
- This creates a Python 3 environment in the location
~/katapult-env/and installs the modulepyserialwhich is required to run the upload script. - Now we must force board to enter the Katapult bootloader and obtain the USB serial address. Start by quickly double clicking the RESET button, you should see the ACT light blinking slowly.
- Next run
ls /dev/serial/by-id/. You should see something likeusb-katapult_rp2040_A1234567898D1234-if00- note that the address contains the wordkatapult. If not, this means either your board did not have Katapult installed or you did not enter the Katapult bootloader properly. Copy the address down for the next step, do not exit the bootloader yet. - Finally run the following but substituting the address with the one you obtained in the previous step. If everything was correct, you should see some write and verification progress followed by
Flash Successat the end.
~/katapult-env/bin/python3 ~/katapult/scripts/flashtool.py -d /dev/serial/by-id/usb-katapult_rp2040_A1234567898D1234-if00As a finally verification, run ls /dev/serial/by-id/. you should see a Klipper USB serial address in the form of usb-Klipper_rp2040_E1234567A12D9835-if00.
¶ Installing the Katapult Bootloader
In this section we will compile and upload the Katapult Bootloader. Note that your board normally ships with Katapult pre-installed and you only need to perform the following operations if Katapult was inadvertently overwritten or lost.
- Login to the Raspberry Pi. We will check and download the Katapult package (if necessary):
test -e ~/katapult && (cd ~/katapult && git pull) || (cd ~ && git clone https://github.com/Arksine/katapult) ; cd ~
- Now we will configure need to configure some options:
cd ~/katapult
make menuconfig
- This will bring us to the configuration menu. Make sure to set the options as below:
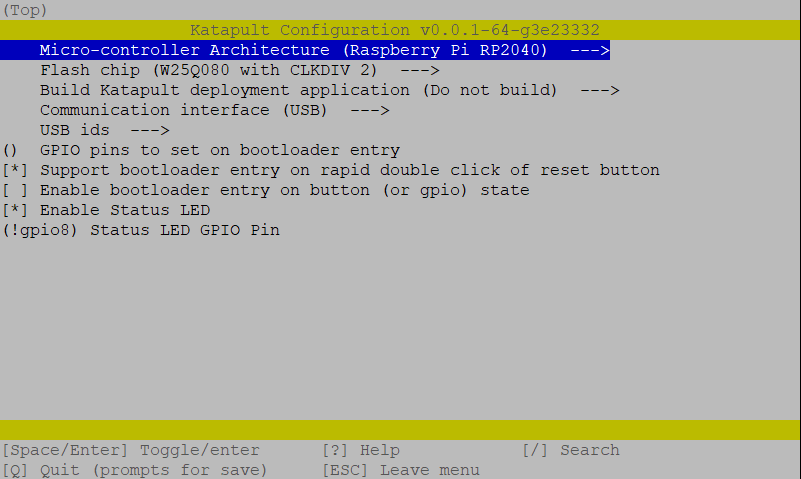
- Enter
Qto quit and confirm withYes when prompted to save. next run the following command to compile and generate the Katapult binary files:
make clean
make
- A binary file called
katapult.uf2will now be created in the location~/katapult/out/. Our next job is to upload this file into the RP2040 MCU on the board. - We now need to reboot the board into system boot mode. This is done in three steps:
- Press and hold both the RESET and BOOT0 button.
- Release the RESET button
- Release the BOOT0 button
- If done correctly, your board should now have entered boot mode and become a sort of semi “thumbdrive”. Run the command
ls /dev/sda*to confirm. You should see something like/dev/sda/ dev/sda1. If you get something likels: cannot access '/dev/sda*': No such file or directorythis means either board didn't enter boot mode or there is a problem with the physical connection between the Raspberry Pi and the board. - We are now finally ready to upload Katapult. Run following commands:
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/pico
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/pico
sudo cp ~/katapult/out/katapult.uf2 /mnt/pico
sudo sync
sudo umount /mnt/pico
- The above commands basically mount the board as a storage drive and copies the katapult binary files into that drive. It then unmounts the drive. If everything went smoothly, you should now be able to see the ACT light located below the BOOT0 button blink slowly. To double check that Katapult is installed, run
ls /dev/serial/by-id. You should see something like:usb-katapult_rp2040_A1234567898D1234-if00which is USB serial address of board running Katapult. A few small details to note here:
- You will only see this address when your board is in Katapult bootloader mode and not in system boot mode or when the board is normally running Klipper.
- You can force the board to enter the Katapult bootloader by quickly double clicking the RESET button on the toolboard. The ACT light blinks slowly in this mode as previously mentioned.
- You will need enter the Katapult bootloader and the Katapult USB serial address to upload Klipper.
- By following the above instructions, you will have uploaded Katapult but erased all other firmware, including any previously installed Klipper firmware.
- Exit the Katapult bootloader by single pressing the RESET button, normally you would enter Klipper firmware. Since you just erased Klipper, you will just re-enter the Katapult bootloader.
- you are now ready to compile and upload Klipper - see the previous section here.